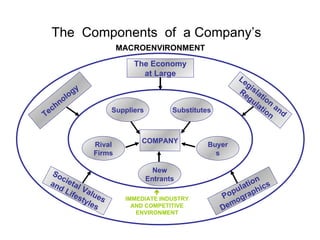
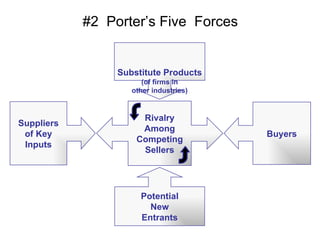
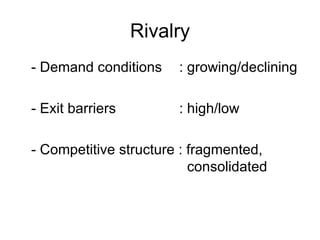
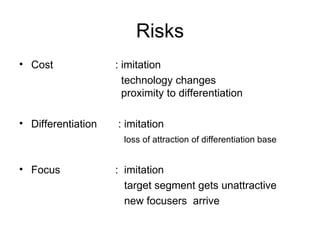
The document discusses the environment and stakeholders of a business. It identifies key external factors such as the economy, technology, socio-cultural values, demographics, and legislation that influence a company. It also examines a company's immediate industry environment including suppliers, buyers, new entrants, and rival firms. Porter's five forces model is introduced to analyze competitive forces in an industry. Different generic competitive strategies such as cost leadership, differentiation, and focus are also outlined.